In a groundbreaking discovery, scientists have achieved a remarkable feat by identifying intricate organic molecules in a galaxy positioned more than 12 billion light-years away from Earth. This extraordinary accomplishment is significant as it represents the furthest known location where such molecules have been detected. The advent of the James Webb Space Telescope, equipped with its exceptional capabilities, along with the meticulous analyses conducted by the research team, has made this breakthrough possible. Through their findings, we gain invaluable insights into the complex chemical interactions that took place within the earliest galaxies of the universe.
Leading the charge in this remarkable scientific endeavor is Joaquin Vieira, an esteemed professor of astronomy and physics at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign. Alongside him is graduate student Kedar Phadke, and together they form part of an international team of scientists collaborating with researchers from Texas A&M University. Their collective efforts are aimed at discerning between infrared signals originating from the massive dust grains within the galaxy and those emanating from the newly discovered hydrocarbon molecules.
Vieira harks back to the genesis of this project, recounting his days as a graduate student dedicated to unraveling the mysteries of elusive galaxies concealed by dust. He sheds light on the extraordinary attribute of dust grains, which possess the capacity to absorb and re-emit nearly half of the stellar radiation generated within the vast expanse of the universe. Consequently, the faintness or complete invisibility of infrared light emitted by distant objects poses a formidable challenge when observed through ground-based telescopes.
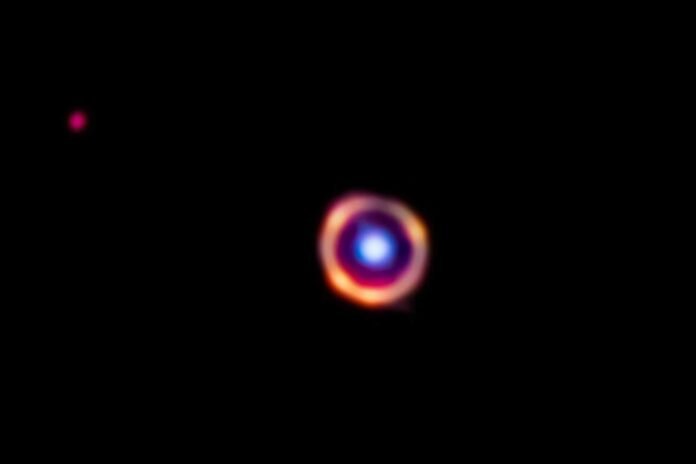
A significant breakthrough in the study occurred with the advent of what researchers fittingly refer to as nature’s magnifying glass—a mesmerizing phenomenon known as gravitational lensing. This natural occurrence materializes when two galaxies align almost flawlessly from Earth’s perspective, causing the light emitted by the background galaxy to undergo distortion and amplification due to the gravitational influence exerted by the foreground galaxy. The resultant effect manifests as a captivating, ring-like structure commonly referred to as an Einstein ring.
The team turned its attention to a specific celestial object named SPT0418-47, initially discovered through the utilization of the National Science Foundation’s South Pole Telescope. This galaxy, cloaked in a shroud of dust, experienced substantial magnification as a result of gravitational lensing, rendering it approximately 30 to 35 times larger in apparent size. Situated an astounding 12 billion light-years away from Earth, SPT0418-47 hails from a time when the universe was a mere 1.5 billion years old, constituting a mere 10% of its present age, as corroborated by the researchers.
Vieira underscores the immense challenge faced by the team before gaining access to the combined power of gravitational lensing and the James Webb Space Telescope. Previously, the actual background galaxy hidden amidst the veil of dust remained elusive, defying resolution by conventional means.
By harnessing the spectroscopic data obtained from the James Webb Space Telescope, the researchers unlocked intriguing insights into the obscured interstellar gas permeating SPT0418-47. The presence of heavy elements indicated that numerous generations of stars had already arisen and perished within the galaxy’s expansive domain. Moreover, the researchers successfully identified a specific compound known as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) among the ensemble of detected molecules. Composed of carbon chains, these organic molecules are regarded as the fundamental building blocks underlying the nascent origins of life. Interestingly, PAH molecules find their earthly counterparts in the exhaust emissions of combustion engines and the aftermath of forest fires.
Phadke passionately expounds on the remarkable implications borne out of their groundbreaking research. The availability of new spectroscopic data enables them to discern the atomic and molecular composition of the galaxy, thereby affording crucial insights into the formation, lifecycle, and evolution of galaxies. Vieira, taken aback by the unexpected nature of this discovery, acknowledges its transformative potential for future observations. He conveys a sense of excitement and anticipation, recognizing that this remarkable work represents just the initial stride toward a much broader and deeper understanding of the capabilities and applications of the James Webb Space Telescope. The researchers eagerly await the unfolding of further developments on this extraordinary journey of discovery.
Vieira expresses his astonishment and gratitude that the very galaxies he once discovered during his thesis are now being observed by the James Webb Space Telescope. He acknowledges the indispensable contributions made by U.S. taxpayers, as well as the unwavering support and funding provided by the National Science Foundation and NASA for the South Pole Telescope and the James Webb Space Telescope. It is these critical instruments that have paved the way for this remarkable discovery, which would have otherwise remained tantalizingly out of reach.
In summary, the detection of complex organic molecules within a galaxy located over 12 billion light-years away represents a monumental achievement in the field of astrophysics. Thanks to the cutting-edge capabilities of the James Webb Space Telescope and the captivating phenomenon of gravitational lensing, scientists have acquired critical insights into the intricate chemical interactions that characterized the earliest galaxies in the universe. The identification of organic molecules at such staggering distances raises the tantalizing possibility of life’s elemental building blocks existing during the infancy of the cosmos. As scientific exploration continues to push boundaries and technological advancements expand our cosmic understanding, the allure and curiosity surrounding the uncharted realms beyond our own planet intensify.
Image credit: J. Spilker/S. Doyle, NASA, ESA, CSA
Follow THE SCIENTUIT on…